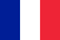
What's this? Psoriasis is a non-communicable skin disease and therefore cannot be infected. It not only affects the skin, but also negatively affects the entire organism. It is characterized by chronic curriculum with periods of deterioration and recovery.
This disease is caused by the immune cells of one's own body, which is an autoimmune disease. These cells rise from deep into the upper layer, causing inflammation, excessive division of epidermal cells, leading to overgrowth, and new small capillaries appear.
Externally, it looks like a red or red spotted patch - psoriatic plaques.
The first signs and symptoms of psoriasis
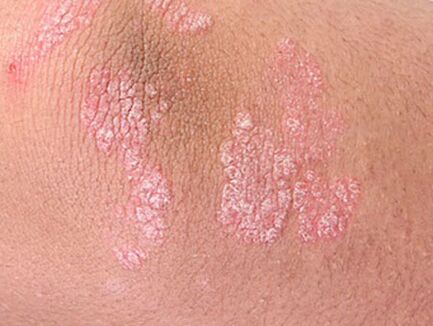
Because of psoriasis - a systemic disease that affects all systems of the body, patients suffer from general weaknesses and rapid fatigue.
The main symptoms of the initial stage of psoriasis are psoriatic rashes and plaques, however, it is accompanied by a person with a disease further development.
They are produced by the acceleration of uncontrolled cellular cells located on the upper layer of the skin-thyroid-forming cells. As new capillaries are enhanced, related cells are formed, and the skin in these areas thickens, obtaining red. This can cause any (even light, yet gentle) drip bleeding to the plaque.
The surface of the plaque is usually covered with grey raids, similar to paraffin. The term "paraffin lake" has even been formed. The plaque consists of dead epithelial cells that accumulate on the surface of the plaque due to impaired rejection processes.
Spots can reach large sizes and merge with each other. Their touch is hot, usually accompanied by severe itching. A comb can cause infection.
As time goes by, nails begin to change. Their surfaces are cut, pits appear, and pink spots are noticeable under the nail plate - the accumulation of liquid, the nails turn yellow and thicken, in the form of poultry claws. All of this happens due to violating the nutrition of nails and blood circulation.
The nail bed experiences excessive deterioration, resulting in a rejection of nails and losses. There is usually a red inflammation border around the nails.
The facet joints are affected by disease and facet joints - accompanied by pain and inflammation.
In addition to plaques, there is psoriasis, which forms papules on the skin - small (about 1 mm) protruding formation similar to a rash. It is usually positioned on the elbows and knees, retained even during remission.
During the improvement process, the patches begin to glow from the middle, taking the shape of the ring and can disappear completely. The pigment area remains in its place.
Psoriasis on the scalp has the same symptoms as in the body. In this case, the hair structure will not change. The rash also covers adjacent areas of the skin - behind the ears, around the neck.
Types of psoriasis
According to the symptoms, the disease is divided into two types: pustule rather than pustule. There are several diseases within these groups.
The form of pustule psoriasis:
- broad sense;
- Conspicuous limbs;
- ladomary;
- Impetigo.
Not pustule psoriasis:
- Common (chronic psoriasis);
- erytro-dermo.
In addition, the following types of diseases are distinguished:
- psoriasis on skin folds and flexion surfaces;
- drug.
Severity form:
- Light (affected by less than 3% of the body surface);
- Average (affecting up to 10% of the body surface);
- Weight (more than 10% of the surface is affected).
Depending on the form of the rash, this type of psoriasis is distinguished:
- Viewpoint;
- Haggard;
- currency.
The development stage of psoriasis, symptoms
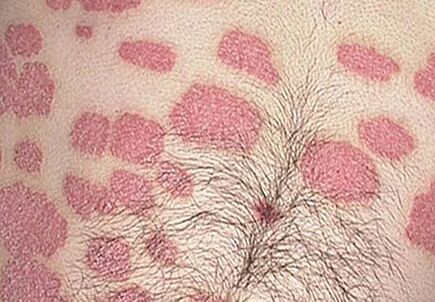
The first batch of plaques appear in areas with dry skin and will never happen where the skin is too wet. First, the appearance of the spots can be seen inside the elbows, under the knees, the boundaries of the hair, and where there are any injuries or frictions. This position is usually symmetrical.
Perform such phases during the disease:
- Progressive (formation of new sites, existing growth, itching, obvious peeling);
- Fixation (slowing or suspending plaque growth, no newly formed spots);
- Regression (reduce or lack of peeling, spots and plaques disappear, and pigmented skin areas appear in their location, with little signs of psoriasis).
There are no special tests to establish the diagnosis. Diagnosis is based on external features. One of these signs will be bleeding that bleeds when the plaque comes into contact.
Another specific sign of psoriasis will be the presence of a pale border around the young papules, not yet covered with scales. This is the vascular reaction of the skin's appearance, which means the progress of the disease.
In severe forms of disease, blood conditions may change. Signs of flow inflammatory processes occur. In some cases, you must perform a biopsy to rule out other skin diseases and confirm the presence of psoriasis.
Effective treatment of psoriasis
In the treatment of psoriasis, topical and internal therapy, physical therapy and hydrotherapy are used.
During the initial mild course of the disease, use medication in the form of ointments. First, use a simple ingredient ointment and face cream, then go to a ointment containing hormones. Creams for psoriasis should be applied only to plaques and spots.
Ointments for psoriasis: An overview of hormones and non-hormonal agents
With the average and severe course of the disease, use internal products that affect the entire body but give the best results. This group includes vitamin A, immunosuppressants, and cell inhibitors.
Physiotherapists bring tangible relief to patients with psoriasis, which can inhibit the development of the disease and sometimes replace the use of certain drugs.
UV irradiation (phototherapy), laser, ultrasound and magnetic therapy, high temperature, electronics, electrophoresis, electrophoresis.
Psoriasis can gain resistance to treatment over time, so it is recommended to change the method (treatment rotation) from time to time.
Psoriasis diet
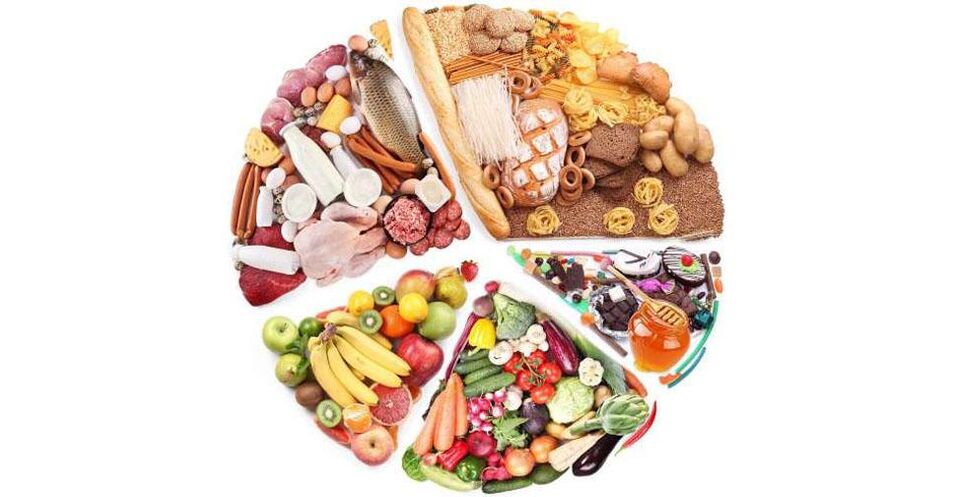

Nutrition should help adjust metabolism and prevent the appearance or exacerbation of skin symptoms. Since almost all patients violate lipid metabolism, low-fat products should be preferred.
Fire and other people's special diets quickly became famous.
When compiling diets, you need to try to follow some simple rules:
- Reject alcoholic beverages;
- Food is up to 6 times a day, little by little;
- Exclude fried foods from your diet;
- Reduce the salt content in foods;
- Do not use the product with the content of dyes, stabilizers and other nutritional supplements if possible;
- Exclude citrus fruits;
- Increase the share of vegetables and cereals in the diet;
- Mandatory use of vegetable oil.
Following these simple rules will help avoid exacerbation of psoriasis and independently form a therapeutic diet.